- Veneer refers to a thin sheet of wood, typically glued onto core panels to produce flat panels such as doors, tops and panels for cabinets, parquet floors and furniture parts.
RELATED VIDEOS
Manufacturing of veneer
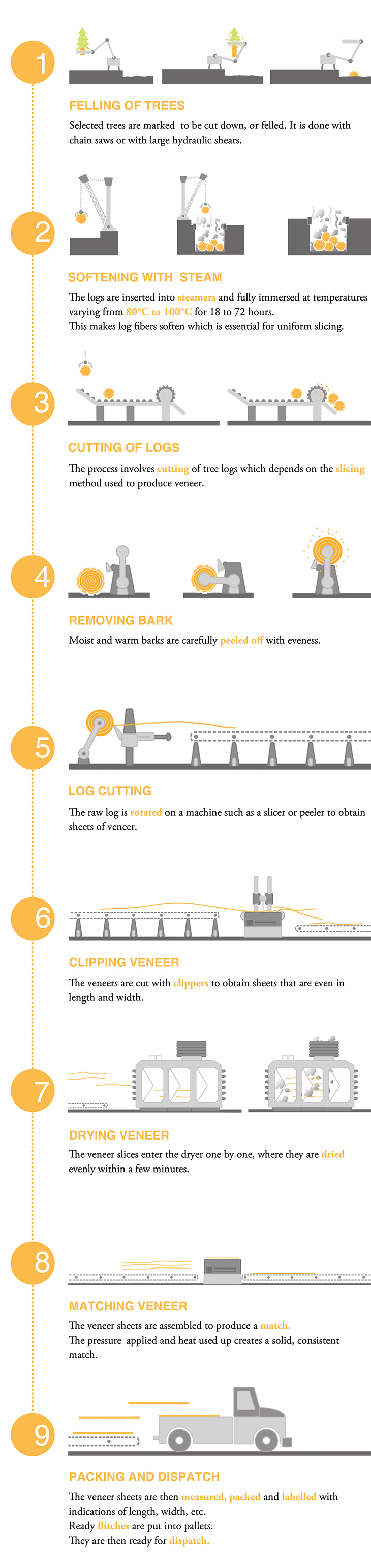
Methods of veneer cutting
1. Rotary Cut Veneer:
Method: The log is rotated around its axis.
Visual effect: Bold, variegated grain pattern.
2. Crown Cut or Plain or Flat cut Veneer :
Method: It is sliced parallel to a line through its centre of the half log.
Visual effect: Light, uniform, variegated pattern with dome shaped cathedrals
3. Quarter Normal Cut Veneer:
Method: The quarter log is mounted on the flitch table such that the log?s growth rings hit the blade at straight angles.
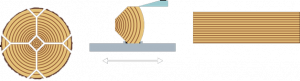
Visual effect: Series of straight lines, striped, straight or variegated pattern.

4. Quarter Rift Cut Veneer:
Method: The cut is done at an oblique angle from the position of the quarter log.
Visual effect: Comb or rift grain effect.
5. Half-round Cut Veneer:
Method: A log is halved and cut on an arc, parallel to its centre.
Visual effect: Cathedrals usually have rounded tops.

Types of veneer matching
Matching can be classified into three categories, each containing several sub-categories:
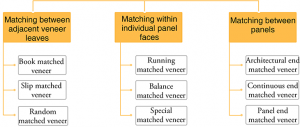
a. Matching Between Adjacent Veneer Leaves
- According to this, individual veneer leaves will be joined together on the face of the panel.
1. Book Matched Veneer
Match: In book matched veneer, alternating pieces of veneer are placed in a fashion that they face each other like the pages in a book.

Visual effect: Balanced, symmetrical pattern.

2. Slip Matched Veneer
Match: Veneer slices are faced in sequence without flipping the pattern.

Visual effect: The joints are not visible if the grain is straight.

3. Random Matched Veneer
Visual effect: Veneer leaves are placed next to each other in an arbitrary manner. Veneer leaves which are matched by color but not by grain pattern are Pleasing matched veneers.

Visual effect: Inconsistent, abstract pattern.

b. Matching Within Individual Panel Faces
- According to this, veneer face is positioned differently.
1. Running Matched Veneer
Match: Each face is assembled from different veneer pieces of unequal widths.

Visual effect:Asymmetrical appearance
2. Balance Matched Veneer
Match: Each face is formed out of even or odd number of pieces of uniform width before trimming.

Visual effect: Balanced, symmetrical appearance.

3. Special Matches
Match: Special matches feature names such as box, diamond, basket weave, sunburst, reverse diamond, reverse box and checkerboard match.

Visual effect: Abstract, balanced appearance
c. Matching Between Panels (Matching Architectural Panels)
- It involves the orientation of finished panels during the construction.
1. Architectural End Match
Match: Leaves are vertically flipped and then horizontally booked or slipped.

Visual effect: Regular grain line continuity

2. Continuous End Matched Veneer
Match: Multiple panels end matched for length using a single length of veneer. This style is used to extend the apparent length of available veneer.

Visual effect: Continuous grain pattern

3. Panel End Matched Veneer
Match: This match has leaves are book or slip matched on panel assemblies.Then the assemblies are broken into sub-assemblies and stacked in an end match.

Visual effect:Pleasing, blended appearance and grain continuity

Properties of veneer
1. Sound Insulation
- Veneers are thin slices with minimal thickness and have negligible effect on the acoustic properties of materials.
- To increase the absorption capacity, holes or slots are made and distributed over the surface area.
2. Moisture Resistance
- Veneers are vulnerable to moisture in outdoors, there are ways to improve moisture resistance and dimensional stability.
- Treat veneers with a solution which results in cross linking of cellulose fibres.
- Thermal treatment is another way to produce moisture resistant veneers.
3. Electrical Conductivity
- Application of oil or wax on wooden flooring ensures that it remains antistatic.
4. Recyclability & Renewability:
- Veneer is a recyclable, renewable material with the lowest impact on energy use and pollution.
- It uses 70% less energy compared to other building materials.
5. Sustainability
- Using veneer over timber extends the use.
General uses of veneer
1. Interiors
- Veneer is primarily a material used to enhance aesthetics of interiors.
- It provides the rich look of solid wood to floor, walls, ceiling and other building elements like doors and windows.
2. Furniture
- It is suitable for furniture decoration in residential and commercial spaces.
3. Artworks
- It can be used to create wooden instruments as well as decorative items.
4. Luxury products
- It is suitable for bespoke products such as wines and chocolate boxes, luxury soap boxes, etc.
5. Miscellaneous
- Its use also diversifies into processed forms such as veneer parquet, wood veneer boards, etc.
Types of veneers
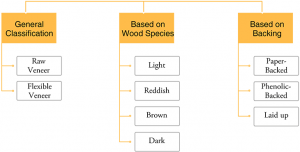
a. General Classification:
1. Raw veneer
2. Flexible veneer
b. Based on Wood Species
1. Light: Maple, Birch, Ash and Alder

2. Reddish: Beech, Cherry, Wild Service Tree and Mahogany

3. Brown: Oak, Teak and Walnut

4. Dark: Wenge, Bog Oak and Macassar

c. Based on Backing:
1. Paper-Backed
- These are veneers that are permanently bonded to a paper backing.
- It is available in large sizes in the form of sheets, as otherwise, smaller pieces are bonded together before adding the backing.
- It is less likely to crack when being applied on curves.
2. Phenolic-Backed
- It is a less commonly used plastic, water resistant resin bonded to the back of a sheet of wood veneer.
- Like the paper-backed veneers, it also has the advantage of being available in sheets, and is also less likely to crack when being applied on curves.
3. Laid up
- Raw veneer that has been bonded together to produce larger pieces.
- It can be laid up to any size, shape or design can be selected.
Available sizes and thickness of veneer
Sizes:
Thickness:
Veneer size in sq.ft |
Veneer size in mm |
| 8x4 | 2449 x 1219 |
| 10x4 | 3048 x 1219 |
| 12x4 | 3658 x 1219 |
- The thickness of the veneer determines its durability.
- The standard thickness of wood veneer measures between 0.5mm and 4mm.
Price range of veneer
Type of Woods |
Prices |
| Teakwood | Rs.120/sq. ft. |
| Oak | Rs. 140 /sq. ft. |
| Beech Wood | Rs.90/sq. ft. |
| Maple | Rs.70/sq. ft. |
Type of Finishes/Polishes |
Prices |
| Mat | Rs.70/sq. ft. ? Rs.80/sq. ft. |
| PU (Poly urethane) | Rs.150/sq. ft. ? Rs.175/sq. ft. |
| Lamination | Rs.350/sq. ft. ? Rs.400/sq. ft. |
Defects in veneer
1. Discoloration
- Dark, mostly due to water drops that condense on iron parts (iron tannate staining).
2. Burls (burrs)
- Small, round or oval buds.
3. Gum
- It is the occurrence of tiny black dots or striations between the annual rings, caused by resin inclusion.
4. Fiddleback (wavy figure
- These are rays or striations running across the grain at a uniform distance.
- This defect can be seen in Walnut, Cherry, Beech, Ash, Maple, Mahogany, Walnut, and Teak.
5. Flashes:
- Striations and rays are observed running in the direction of growth.
6. Silver figure (flake):
- Light-coloured, slightly iridescent dots, caused by cutting across wood (xylem) rays.
7. Blisters:
- Light-coloured round or oval spots.
8. Resin pockets:
- Identified by dark dots and striations running along the annual rings, formed as result of rein deposits.
Advantages of veneer
1. Aesthetics like Natural Wood at Lower Costs
- Wood veneers are excellent alternatives to natural wood. They imitate the appearance of natural wood, but at much lower costs.
2. Flexibility in Design
- Each wood veneer sheet is distinctive as each tree is unique.
- This makes for endless design possibilities with furniture and interior elements.
3. Increased Strength and Durability
- Application of wood veneer sheets to engineered woods strengthens and increases their durability
- Veneers resist warping and fragmentation and last longer than laminates
4. Eco-Friendly
- It is a natural, environment friendly material which can easily be recycled.
- Wood veneers help in better utilization of wood, since very thin layers of wood are used for decorative purposes.
5. Non-toxic
- Veneers are generally non-toxic.
Disadvantages of veneer
1. Vulnerable to Water Damage
- Prolonged exposure to water can damage veneers.
- Application of a sealant over the veneer protects its surface from wet conditions.
2. More Maintenance
- Wood veneers require more maintenance and they need to be polished periodically.
3. Cannot be Repaired
- Once damaged, wood veneer cannot be repaired, unlike natural wood furniture which can be easily repaired by sanding several times.
4. Formation of Cracks
- Wood veneer is laid on MDF or plywood which has a different expansion and contraction rate than the veneer itself.
- This uneven expansion and contraction results in the formation of cracks.