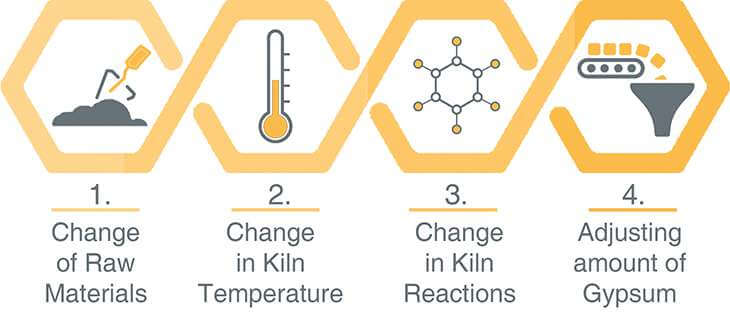
There are different types of cement manufactured to meet different physical & chemical requirements for specific construction projects by altering following ingredients while manufacturing:
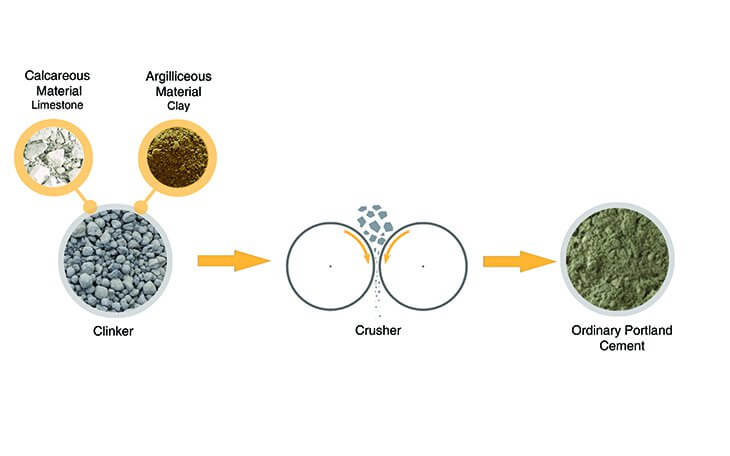
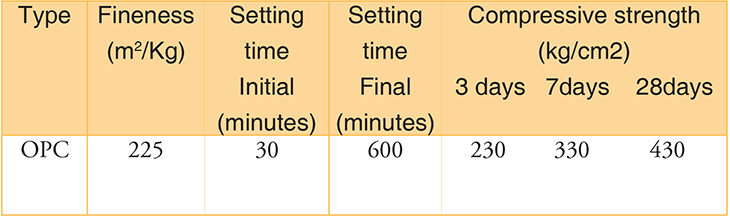
1. Ordinary Portland Cement
- It is the most common type of cement.
- It is used for all ordinary purposes such as making concrete, mortar, etc.
- OPC is available in three different grades namely grade 33, 43 and 53.

Composition of Ordinary Portland Cement
- It is manufactured by mixing limestone/chalk with shale/clay to form clinker which is then finely crushed to form grey color cement.
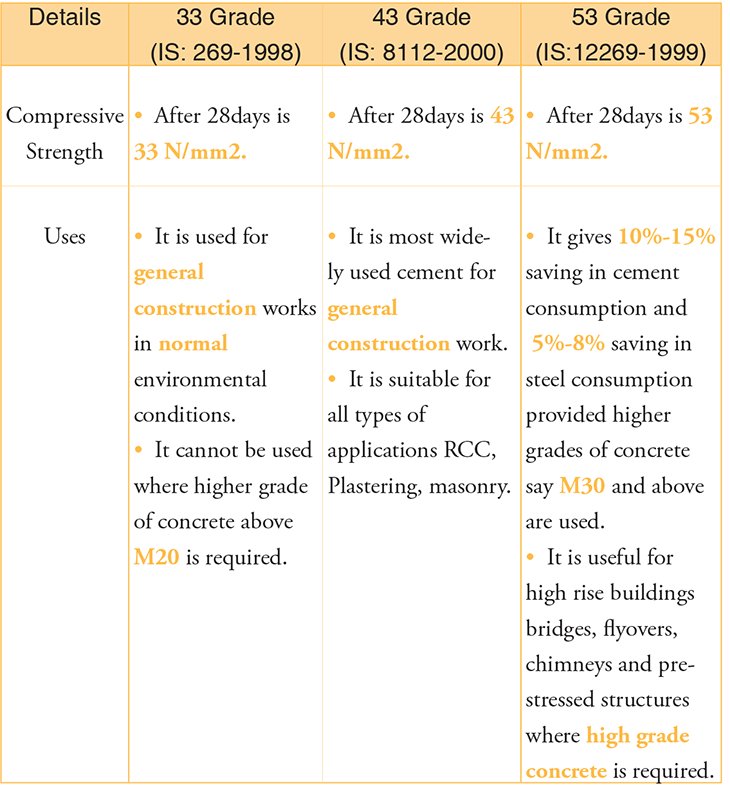
Grades of Ordinary Portland Cement
- It is available in three different grades in India as:
- 33-grade (IS: 269' 1998),
- 43-Grade (IS: 8112' 2000)
- 53-grade (IS: 12269' 1999)
Properties of Ordinary Portland Cement
- It has an adequate resistance to dry shrinkage and cracking, but less resistance to chemical attack.
- It has a medium rate of strength development and heat generation.
Application of Ordinary Portland Cement
- This cement is suitable for all type of concrete construction.
- It is widely used for the construction of high-rise buildings, roads, dams, bridges, flyovers, etc.
- It is also is used for making grouts and mortars.

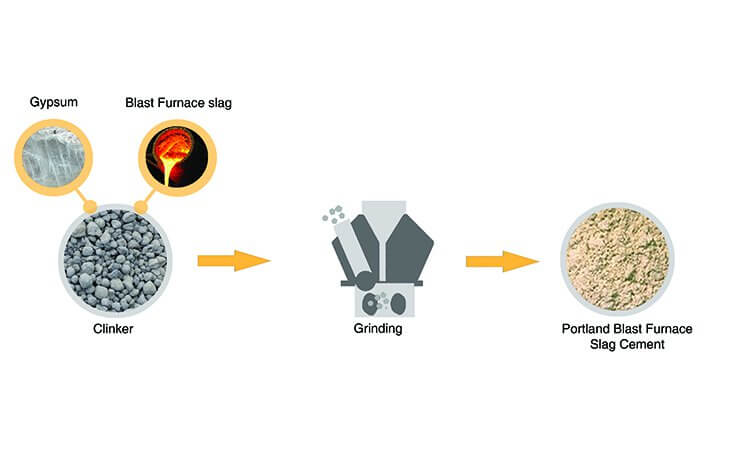
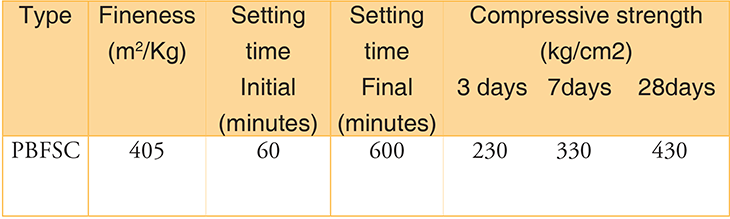
2. Portland Blast Furnace Slag Cement (IS: 455)
- It is the mixture of ordinary Portland cement and fine granulated blast furnace slag.
- It contains 25-65 percent (by weight) of blast furnace slag.

Composition of Portland Blast Furnace Slag Cement
- It is manufactured by grinding clinker and specific amounts of blast furnace slag together.
- A small percent of gypsum is also added for controlling its setting time.
Properties of Portland Blast Furnace Slag Cement
- They possess better work ability, cohesiveness, and plasticity.
- These qualities are explained to be due to lesser specific gravity and greater specific surface area of slag cement.
- They have better resistance to sulfates of alkali metals, alumina, and iron.
Application of Portland Blast Furnace Slag Cement
- It is better suited for structures meant for water retaining such as retaining wall, rivers, ports, tunnels for improvement in impermeability.
- Used in mass concreting works such as dams, foundations which require low heat of hydration.

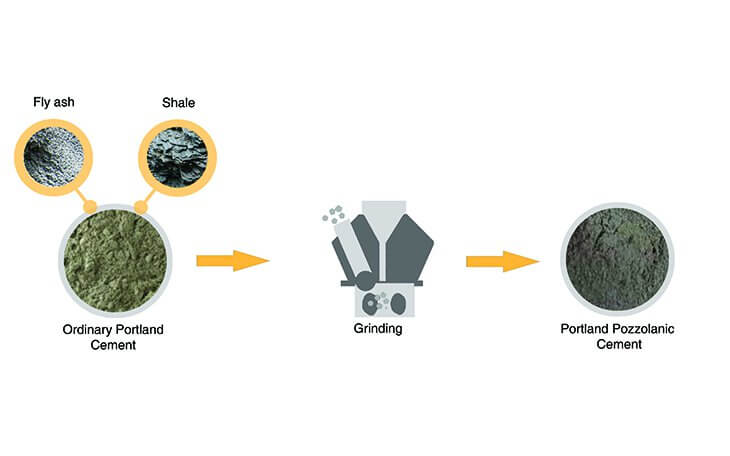
3. Portland Pozzolana Cement (IS: 1489)
- It is a variation of Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC), which includes a mixture of pozzolanic materials, OPC and gypsum.

Composition of Portland Pozzolana Cement
- It is manufactured by adding pozzolanic materials such as fly ash, shales, clays etc. with Ordinary Portland cement.
Properties of Portland Pozzolana Cement
- The pozzolana cement has many properties similar to Ordinary Portland Cement. But it also offers some additional properties, which are given below:
- It produces less heat. Due to this property, it can be used in mega projects.
- It offers greater resistance to sulfates and corrosive actions of sea water.
Application of Portland Pozzolana Cement
- Its properties make it more useful for construction near or along the coast and also in sulfate soil.
- It can also be used in sewage works and for underwater construction.

4. Rapid Hardening Cement (IS: 8041)
- Rapid hardening cement is a special type of cement that achieves high strength in less time.
- It is also called as High-Early Strength Portland Cement.

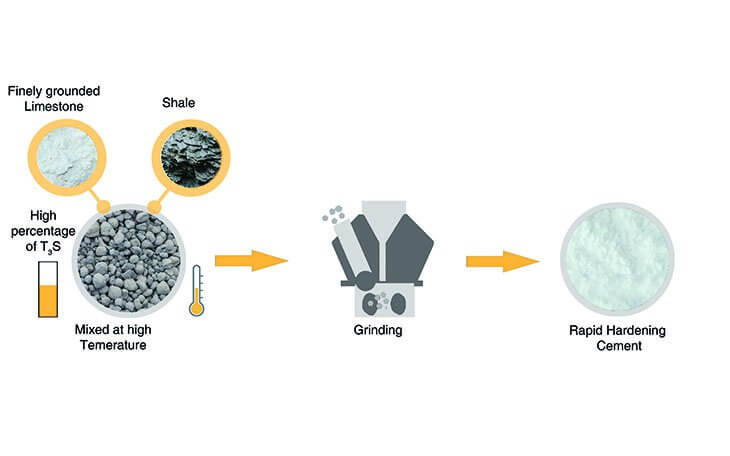
Composition of Rapid Hardening Cement
- It manufactured by combining lime stone (finely grounded) and shale at high temperature.
- It contains high percentage of Tricalcium Silicate (C3S)
Properties of Rapid Hardening Cement
- It attains maximum strength with-in 24-72 hours.
- The strength of rapid hardening cement at the 3 days is similar to 7 days strength of OPC with the same water-cement ratio.
- Relatively high proportion of limestone and fine grained helps in quicker and complete hydration of cement particles during setting and helps in gaining early strength.
Application of Rapid Hardening Cement
- It is used in those types of projects, where quick hardening is required.
- In precast concrete, when the form work to be remove early
- It is also used when the roads or airfield to be repairs, and the roads can throw open to traffic quickly.
- It can be used in the cold weather concreting.

5. Extra Rapid Hardening Cement
- It accelerates the setting and hardening process.

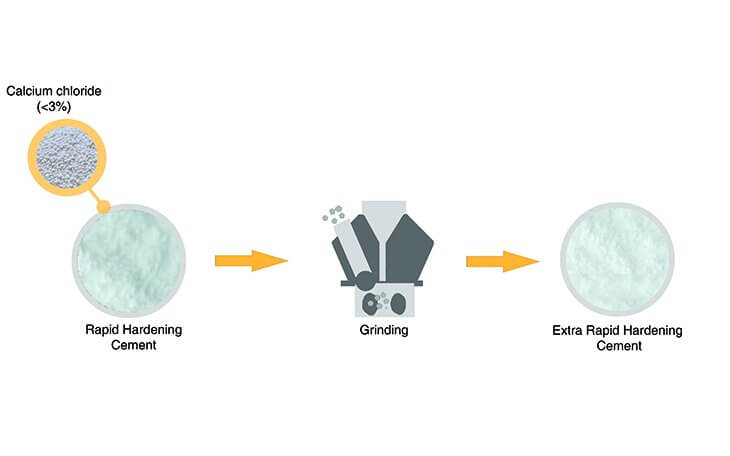
Composition of Extra Rapid Hardening Cement
- It is manufactured by Inter grinding Calcium Chloride (CaCl2) with Rapid Hardening Cement.
- The percentage of Calcium Chloride during the manufacturing process should not exceed 3%.
Properties of Extra Rapid Hardening Cement
- The gain of strength disappears with the age.
- It should be transported, placed, compacted and finished within 20 minutes after mixing .
Application of Extra Rapid Hardening Cement
- It is used for repair and maintenance, eg, fence posts, setting manholes, repairs to paths and steps.
- It is suitable for concrete, mortar, rendering and floor screeds.

6. Acid Resistant Cement
- This cement has good resistance to action of acid.

Composition of Acid Resistant Cement
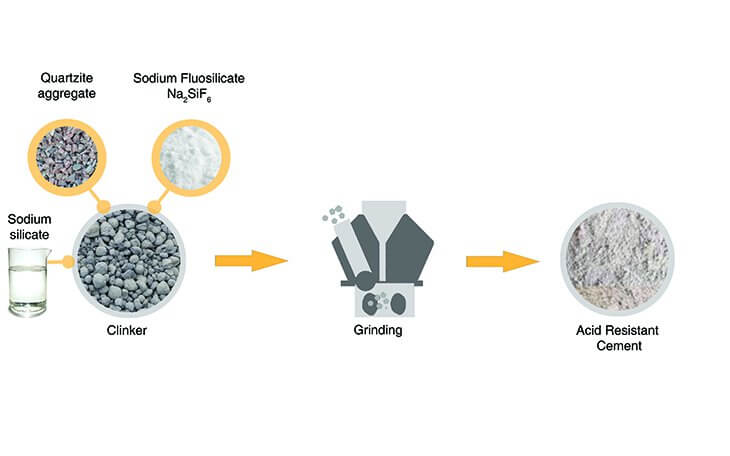
- Acid-resistant cement is composed of the following:
- Acid-resistance aggregates such as quartz, quartzites, etc.
- Additive such as sodium fluosilicate Na2 SiF6
- Aqueous solution of sodium silicate or soluble glass.
Properties of Acid Resistant Cement
- The addition of additive sodium flousilicate accelerates the hardening process and it also increases resistance of cement to acid and water.
Application of Acid Resistant Cement
- It is used for acid-resistance and heat resistance coatings of installations of chemical industry.

7. Sulphate Resisting Cement (IS: 12330)
- This cement is highly sulphate resistant caused due to low C3A content.

Composition of Sulphate Resisting Cement
- It is manufactured with less than 5% tricalcium aluminate C3A to withstand Sulphate attacks.
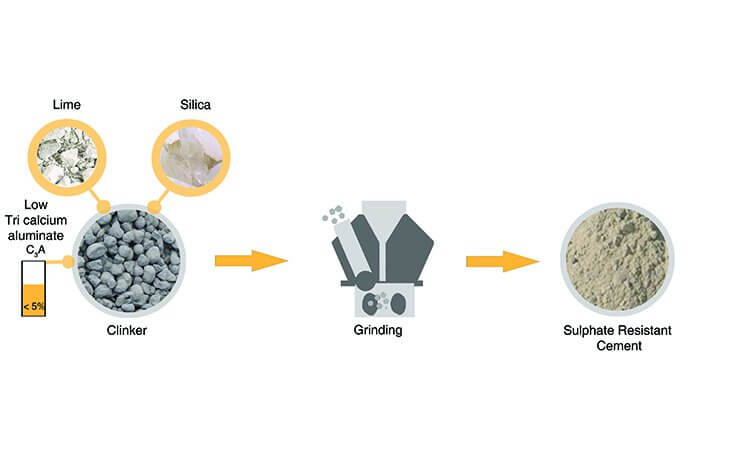
Properties of Sulphate Resisting Cement
Its low heat of hydration helps to avoid shrinkage cracks.
Application of Sulphate Resisting Cement
- It is used in construction exposed to severe sulphate action by water and soil in places like canals linings, culverts, retaining walls, siphons etc.
- It is used to reduce the risk of sulphate attack on concrete and thus is used in construction of foundations where soil has high sulphate content.

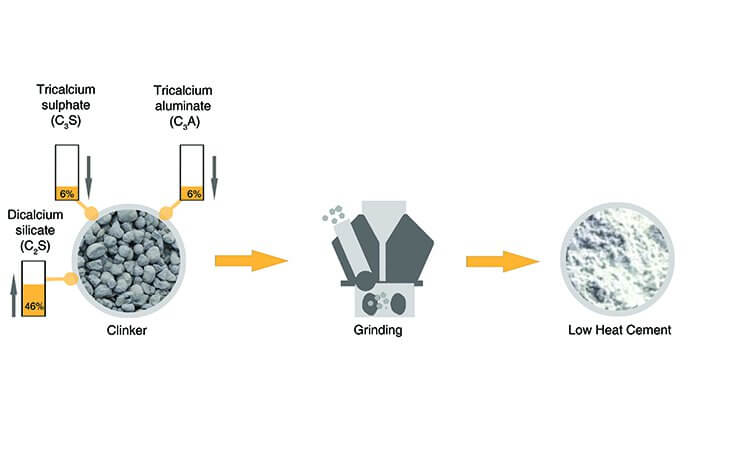
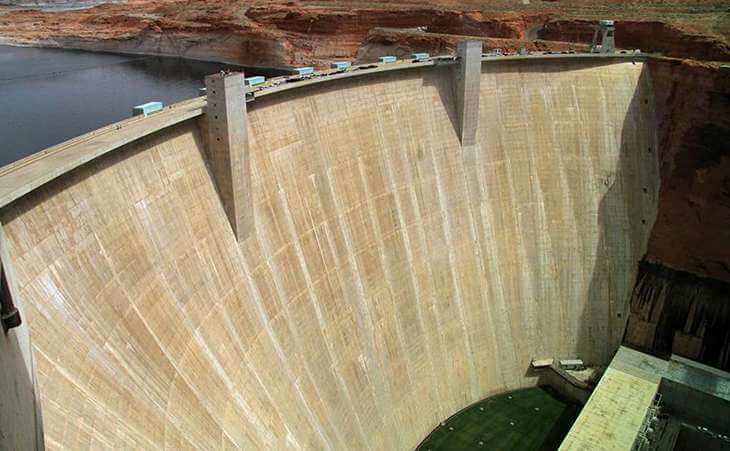
8. Low Heat Cement (IS: 12600)
- It is a type of cement which generates low amount of heat or hydration during setting and hardening.

Composition of Low Heat Cement
- It is prepared by maintaining the percentage of compounds evolving maximum heat of hydration such as tricalcium sulphate (C3S) tricalcium aluminate (C3A) below 6% and by increasing the proportion of dicalcium silicate C2S by 46%.
- It is resistant to sulphate, rupture, anti-seepage.
- It is also resistant to sulphate attack on reinforcement majorly in concrete pipes.
Application of Low Heat Cement
- It is used in mass concrete construction like dams, as the low heat of hydration prevents the cracking of concrete due to heat.
- It is used to make the road and workroom surface of factories such as chemical plants and sulphuric acid factories.

9. Hydrophobic Cement (IS: 8043)
- It contains admixtures which decreases the wetting ability of cement grains.

Composition of Hydrophobic Cement
- It is manufactured by mixing admixtures like acidol, oxidized petrolatum, napthalene soap which forms layer and act as water repellent.
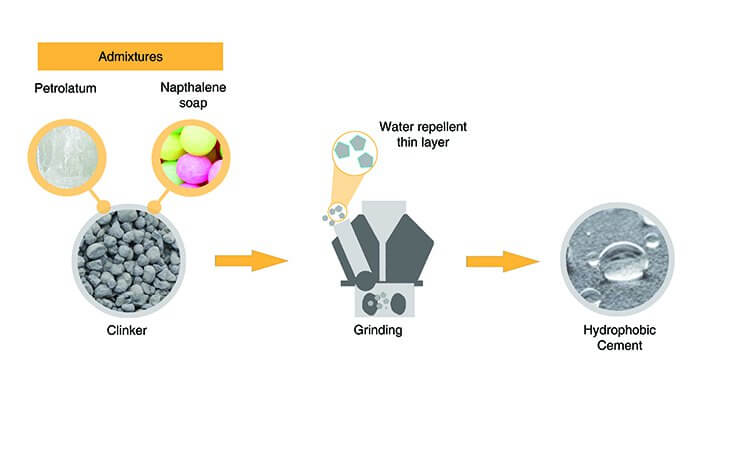
Properties of Hydrophobic Cement
- Its strength after 28 days is equal to that of Ordinary Portland Cement.
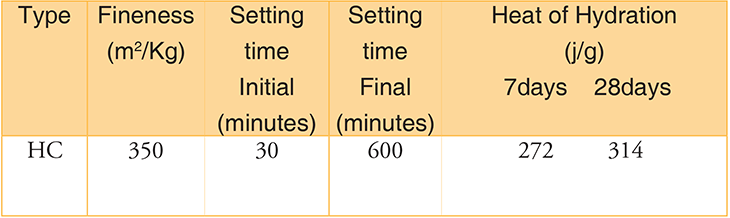
Application of Hydrophobic Cement
- It can be used in the construction of water structures such as dams, spillways, or other submerged structures.
- It can be used in extremely wet climatic conditions.
- It is majorly used in the tunnel construction as the underground repairs are difficult and costly.
- It is also used in the structures that are exposed to rain or rain puddling, such as green roofs, other kinds of roofs, parking structures, and plazas.

10. Quick Setting Cement
- It is the types of cement which sets quickly.

Composition of Quick Setting Cement
- It is produced by following controls in the manufacturing process to accelerate the setting time of the cement:
- The quantity of retarding agents like gypsum is reduced.
- The quantity of alumina rich compound is reduced.
- The clinker is ground to extreme fineness.
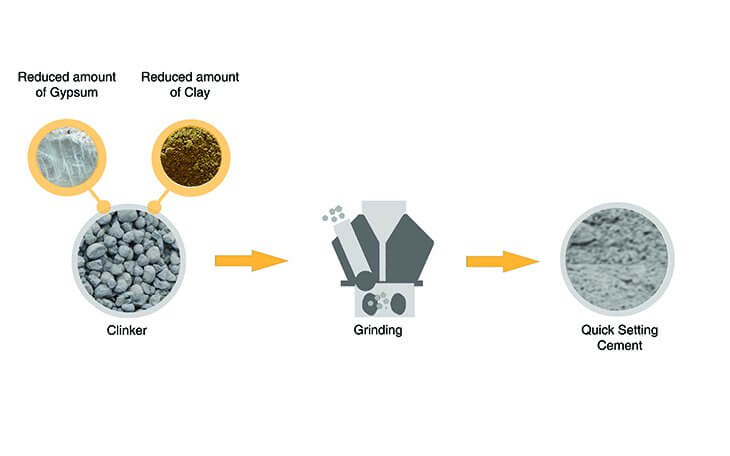
Properties of Quick Setting Cement
- It sets into a stone like mass within a period of fewer than 30 minutes.
Application of Quick Setting Cement
- It is majorly used where quick strength is needed in short span of time.
- It is used while constructing piers for bridges and other structures in running or standing water.

11. Air En-training Cement
- It is special cement which has air bubbles introduced in the cement that provides the space for expansion of minute droplets of waters in the concrete due to freezing and thawing.
- It protects from cracks and damage of concrete.
Composition of Air En-training Cement
- It is manufactured by adding some indigenous air en-training agents such as glues, resins, sulphates, etc., during the grinding stage of clinker.
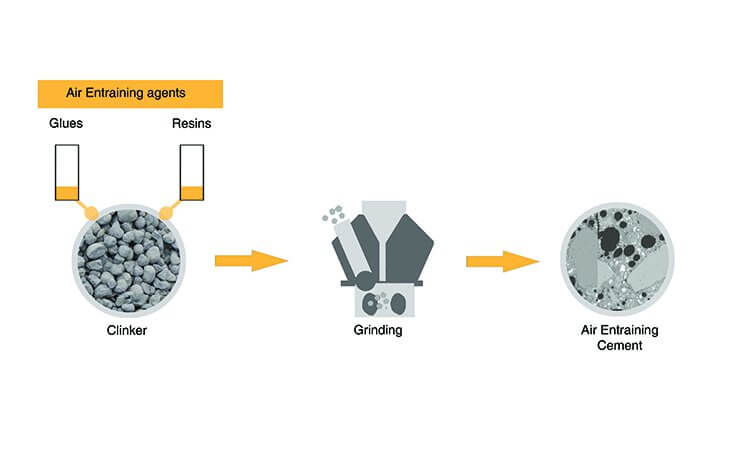
Process of Air En-training Cement
- Here are the ways of incorporating air in concrete:
- Using gas forming materials as aluminium powder, zinc powder and hydrogen peroxide.
- Using surface active agents that reduces surface tension.
- Using cement dispersing agents.
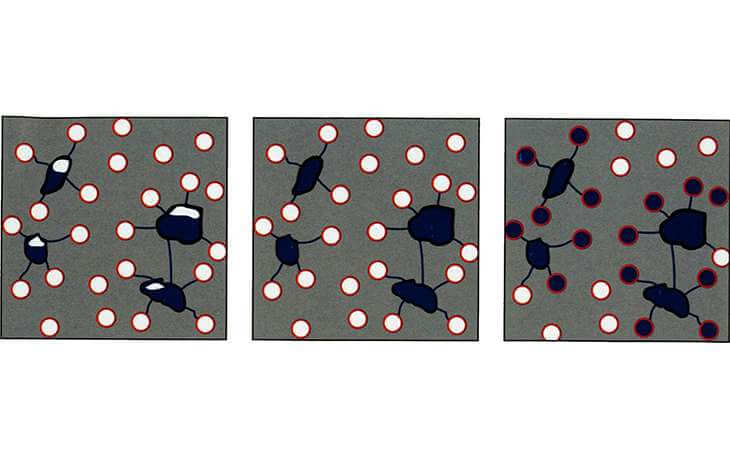
Properties of Air En-training Cement
- It is used to improve the work ability of concrete with smaller water-cement ratio.
- It improves the frost resistance of concrete.
- It is also resistant to sulphate and alkali-silica reactivity.
Application of Air En-training Cement
- It is used where concrete needs adequate durability against cycles of climatic freezing and thawing.

12. Masonry Cement (IS: 3466)
- Masonry cement is specially formulated and manufactured to produce masonry mortar.

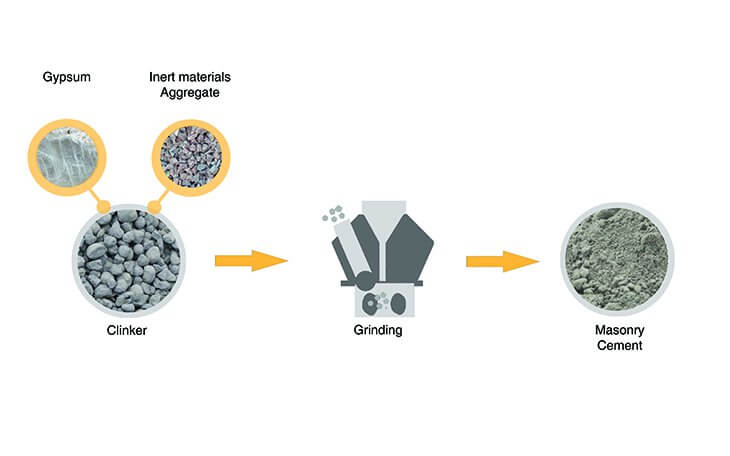
Composition of Masonry Cement
- It is a product obtained by inter-grinding a mixture of Portland Cement clinker with inert materials (Non-pozzolanic), gypsum and air en-training plasticizer.
Properties of Masonry Cement
- It has slow hardening process.
- It also improves work ability.
Application of Masonry Cement
- It used use in brick, block, and stone masonry construction.
- It is also used to produce stucco or plaster.

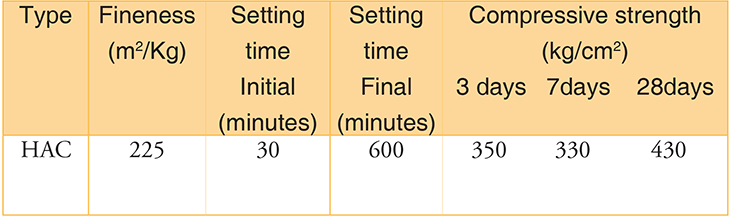
13. High Alumina Cement (IS: 6452)
- It is the type of Cement which contains alumina in considerably larger proportions than normal cement.
- It is also known as calcium aluminum cement.

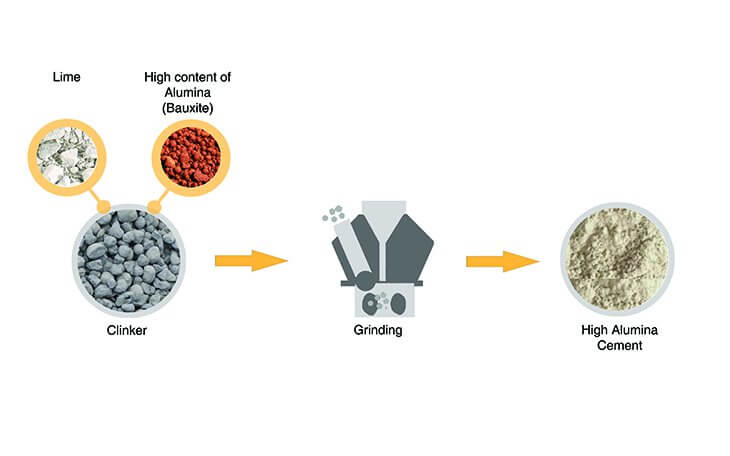
Composition of High Alumina Cement
- It is manufactured by grinding the clinkers of Alumina (Bauxite) and Calcareous material (Lime) by fusing or splintering process.
- The total alumina content is generally above 32 percent.
- No other raw material is added, not even gypsum is mixed with the clinker during grinding.
| Constituents | Content Percentage (%) |
| Silica | 3-8 |
| Alumina | 37-44 |
| Lime | 36-40 |
| Iron Oxide | 9-10 |
| Titanium | 1.5-2 |
| Magnesium | 0.5-1 |
| Insoluble Residues | 1 |
Properties of High Alumina Cement
- It is resistant to the corrosive action of acids and salts of seawater.
- They react quickly with lime.
- It attains high strength and heat of hydration.
- It can withstand high temperature.
Application of High Alumina Cement
- It is also used in refractory concretes where it requires more strength at very high temperature.

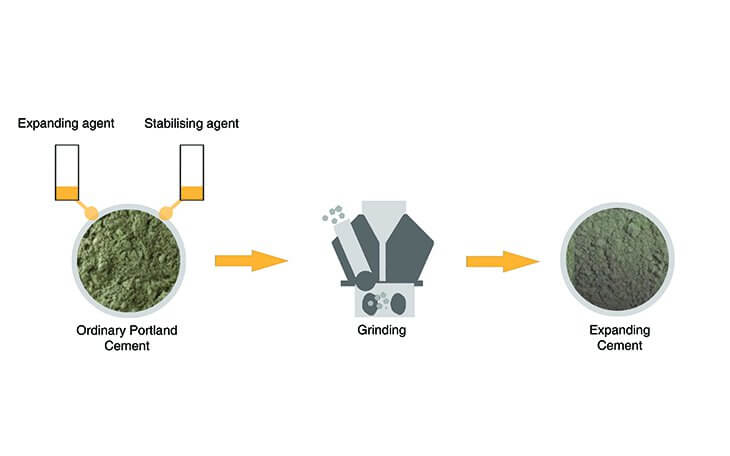
14. Expanding Cement
- It is a type of cement which expands and whereas other cements shrink.

Composition of Expanding Cement
- It is produced by adding an expanding medium like sulpho-aluminate and a stabilizing agent to the ordinary cement.
Properties of Expanding Cement
- These types of cement have the quality to expand slightly with time, but they do not shrink during and after the time of hardening.
Application of Expanding Cement
- It is mostly used for grouting purposes in anchor bolt and prestressed concrete ducts.
- It is also used for repairing the damaged concrete surfaces.

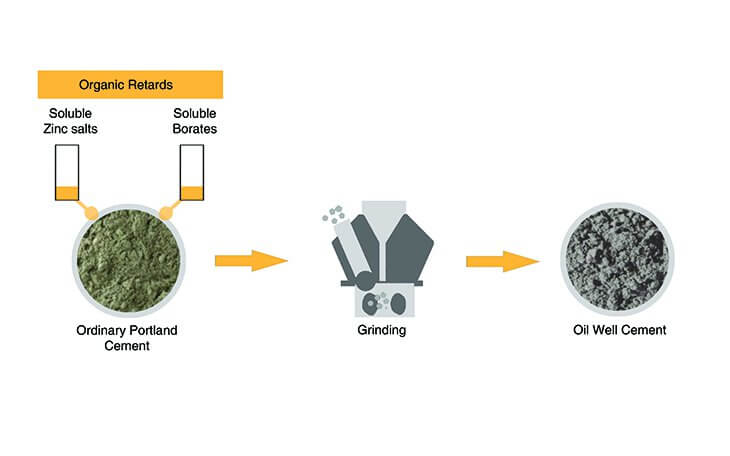
15. Oil Well Cement (IS: 8229)
- It is designed for cementing offshore and onshore wells under high pressure and temperature.

Composition of Oil Well Cement
- It is usually consist of Portland or pozzolanic cement with special organic retarders to prevent the cement from setting too quickly.
Properties of Oil Well Cement
- It prevents the cement from setting too quickly.
- There are no chemical effect of oils.
Application of Oil Well Cement
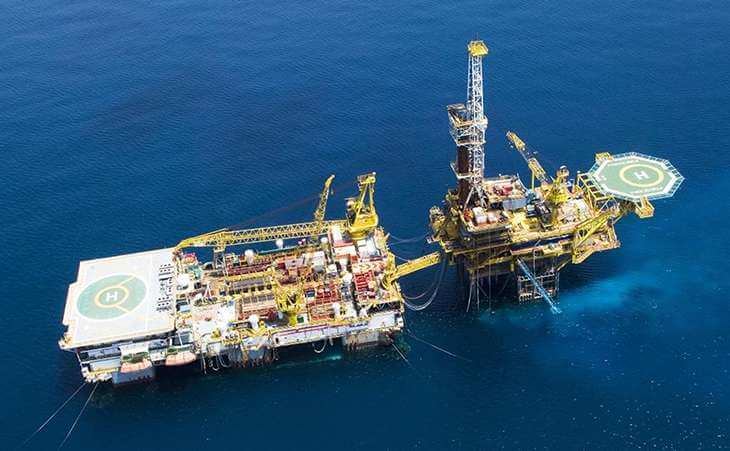
- It is used for cementing work in the drilling of oil wells where they are subject to high temperatures and pressures.
- Its cement slurries are used to protect casing from damage from surrounding water.

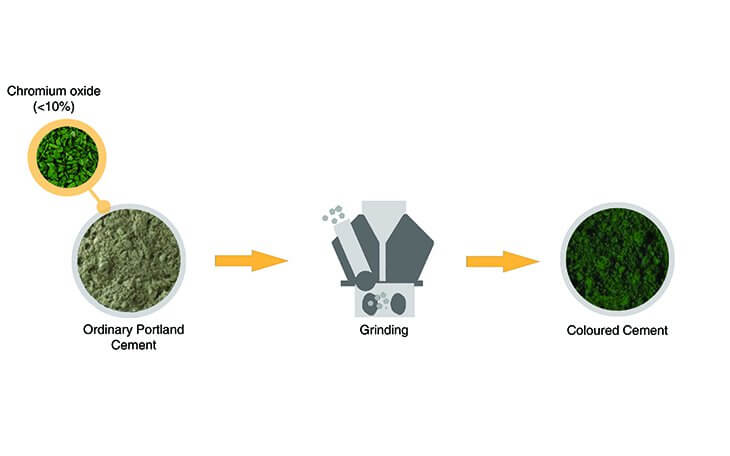
16. Coloured Cement
- The cement of desired colour may be obtained by intimately mixing mineral pigments with ordinary cement.
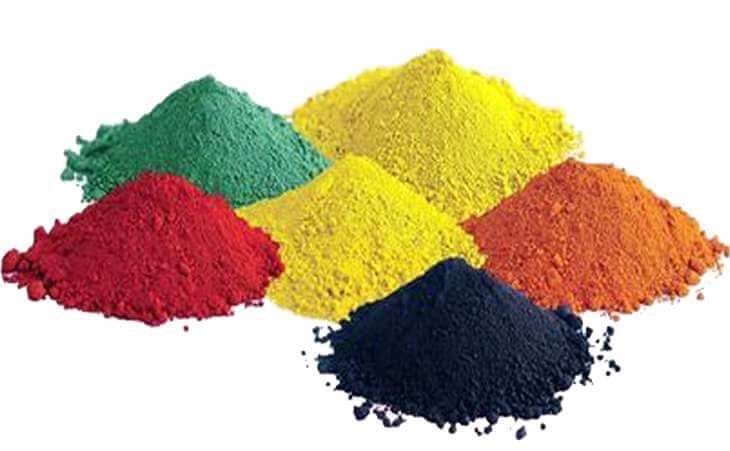

Composition of Coloured Cement
- It is manufactured by mixing colour pigments in a definite proportion with Portland Cement.
- The amount of pigment used depends upon the shade of the desired colour (generally less than 10 per cent by weight).
- The following pigments are used to obtain coloured cement:
| Pigment | Colour |
| Chromium oxide | Green |
| Cobalt | Blue |
| Iron Oxide | Shades of Red, Brown and Yellow |
| Manganese dioxide | Black and deep Brown |
Properties of Coloured Cement
- The amount of colouring material may vary from 5 to 10 percent.
- If this percentage exceeds 10 percent, the strength of cement is affected.
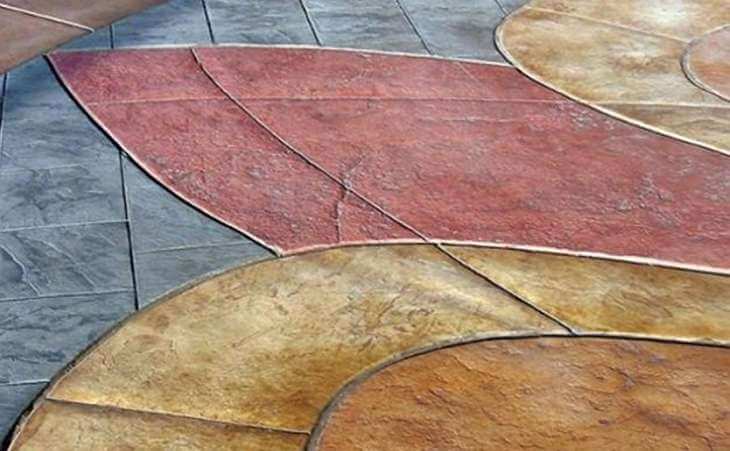
Application of Coloured Cement
- It is used for external finishing of walls and floors, manufacture of tiles and precast stones.
- It is also used for garden paths, swimming pools, and sport courts.

17. White Cement (IS: 8042)
- It is same as the Ordinary Portland Cement except the color.

Composition of White Cement
- It is prepared from raw materials free from colouring ingredients Iron oxide, manganese oxide or chromium oxide
- The cement is burnt by oil fuel instead of coal.
- It has quick drying process.
- It possesses high strength.
- It has superior aesthetic values.
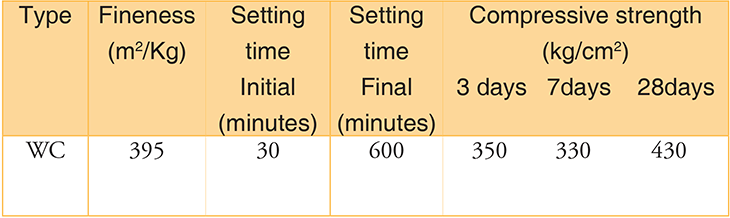
Application of White Cement
- It is used for floor finish, plastering, pointing of masonry, manufacture of precast stones, tiles, runway markings.
- It is used for prestige construction projects and decorative works.
- The miscellaneous applications of white cement are in swimming pools where it replaces the use of glazed tiles.

Difference between OPC and PPC
1. Composition
| Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) | Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) |
| OPC is produced simply by mixing limestone/chalk with shale/clay to form clinker which is then finely crushed to form grey color cement. | It is manufactured by adding pozzolanic materials such as fly ash, shales, clays etc. with Ordinary Portland cement. |
2. Raw Material
| Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) | Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) |
|
|
3. Properties
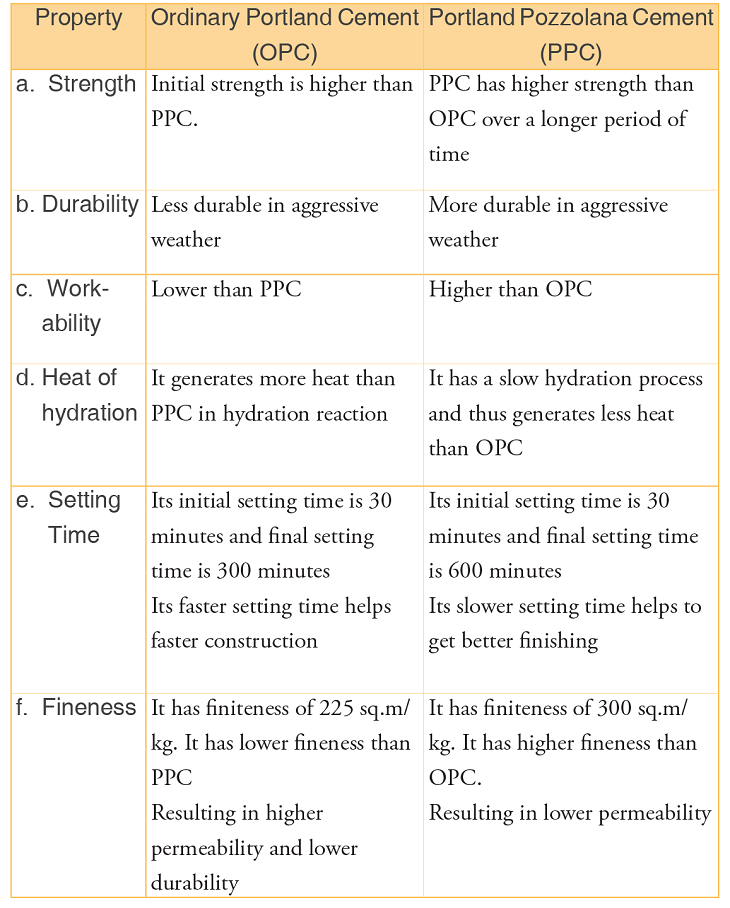
4. Grades
| Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) | Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) |
| 33 Grade, 43 Grade, and 53 Grade OPC cement are available | No specified grade of PPC cement is available. |
5. Environmental Impact
| Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) | Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) |
| It emits CO2 during the manufacturing process. | It constitutes industrial and natural waste which makes it eco-friendly. |
6. Application/ Uses
| Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) | Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) |
|
|
7. Cost
| Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) | Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) |
| Costlier | Cheaper |
8. Identification
| Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) | Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) |
| The ISI mark on this cement bag is black in color. | The ISI mark on this cement bag is red in color. |

Tips before Purchasing Cement
1. ISI Mark
- It is mandatory for any cement manufacturer to have ISI mark. Hence, the bag must carry the ISI mark.

2. Manufacturing Date
- Check the date, week number and year of the manufacturing which is printed on the cement bags.
- Avoid purchasing cement bags manufactured before 3 months of the purchase date as strength of cement decreases with over period of time.

3. Manufacturer
- Check for the manufacturer's name or trademark on the bag

4. Type of Cement
- Check for the cement type and grade on cement bag.

5. Bag Stitching
- Check the stitching of cement bag and ensure that the cement bag has not been re-stitched.