Site analysis is assessing the site and drawing inferences to aid further design conception and implementation.
Why there is a need of Site Analysis?
- The assessment provides the relevant information regarding the environment, natural and artificial features of the site.
- This ought to be used as starting process for the design process.
Site analysis aids in the following ways :
- Avoiding inappropriate design responses
- Legal Applications
- Discovering interrelationships
- Greater efficiency when designing factors
COMPONENTS OF SITE ANALYSIS
- Location
- Neighborhood context
- Climate
- Site
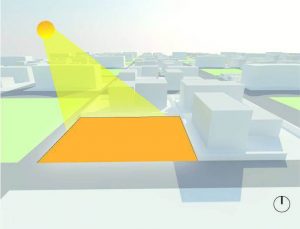
1. LOCATION:
- To understand the relation of site with region and their influence on it.
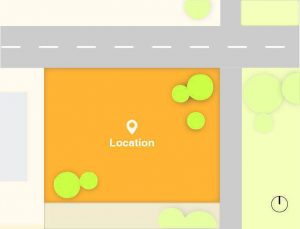
Components of Location:
- State
- City
- Site
a. State:
- To study site at regional level which gives information about:
Factors:
- Historical and cultural aspects
- Resources
- Seismic zone
b. City:
- To study the site at the local level comprising of following:
Factors:
- Geology
- Topography
- Climate
- Geo-hydrology
- Landmarks
c. Site:
- To study immediate or urban context (Paths, Edges, Districts, Nodes, Landmark) to site.
Factors:
- Street name/ address Approach
- Orientation
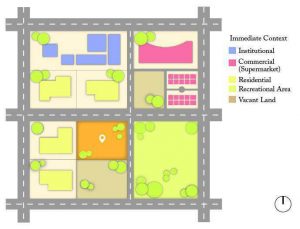
2. NEIGHBORHOOD CONTEXT :
- Immediate surrounding and it may include important factor around the site in its proximity.
- To identify and analyse the various factors in the vicinity that could affect the site's built environment.
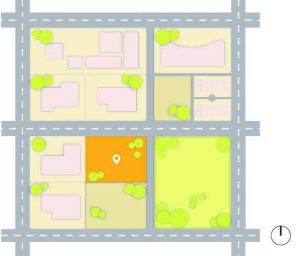
- Immediate context
- Circulation
- Sensory
a. Immediate context
- It refers to all activities which are taking place around the site w.r.t allocation and development.
- To understand the influence of surrounding zoning on site w.r.t users and activities.
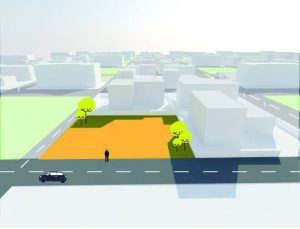
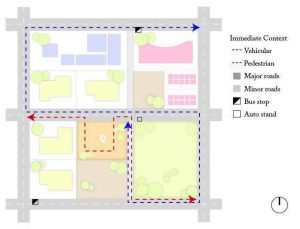
b. Site and Surrounding Circulation
- Movement pattern on and around the site.
- To understand accessibility to the site.
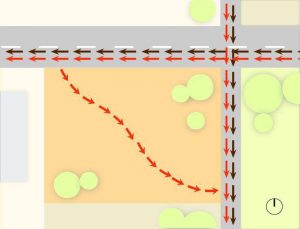
Factors of site and surrounding circulation:
Vehicular
- Bus routes
- Traffic generators
Pedestrian
- Pathways
- Footpaths
Road networks
- Widths
- Major, minor streets
Sensory
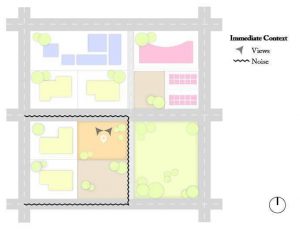
- Observation of audio visual stimuli to and from the site and to take its advantage.
- To judge the relative desirability of sensory conditions on site.
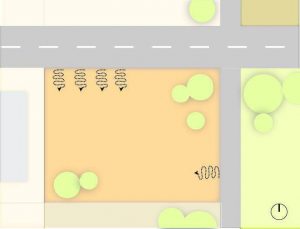
Factors of sensory:
- Visual/Views
- Noise
- Odour

- It is hereby explained through a residential site example:
3. CLIMATE:
- Mean weather conditions over a period of time
- To harness prevailing climatic conditions for creating comfort conditions
- Protect space and building from prevailing winds, cold and from down pour- rain and snow
- Efficient daylight into space and building
- Shade and exposure to sunlight via openings
- Durability and optimum usage of materials
Components of Location:
- Macro Climate
- Micro Climate
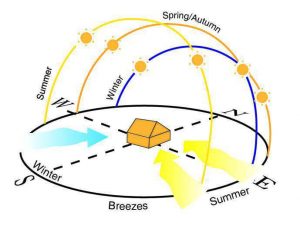
Macro Climate
- Overall climate of the region.
Factors which affect macro climate:
- Temperature
- Relative humidity
- Wind direction
- Rainfall
Micro Climate
- Immediate local climatic conditions
Factors which affect micro climate:
- Topography
- Water bodies
- Vegetation
- Construction materials
Note: A Special features like water bodies, green and open spaces near the site affect the microclimate, So allocation of activities on the site should be done accordingly
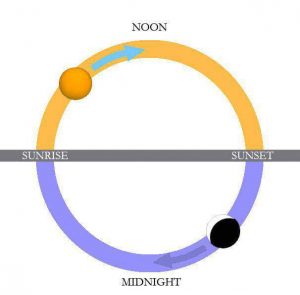
How to study climate?- Macro Climate: Climatic information such as rainfall, snowfall, wind directions, temperatures, sun path, all assessed during the different times of the year.
- Micro Climate: To analyse the micro climate according to the occupancy or usage of the project
- Diurnal temperature of the day should be analysed.
 B. A School
B. A School
- The analysis should be done for the first quarter of the day.

4. SITE:
- To analyse different aspects of site on and around it.
Components of site:
- Size and by laws
- Natural physical features
- Man made features
Size and by laws
- Dimensional aspects and legal verification of site like Building by laws, Sustainable by laws, etc.
- To ensure the orderly development of site.
- Sufficient ventilation and air.
- No building blocks the lighting and ventilation of neighbors.
- Health and comfort conditions.

Factors of Size:
- Dimensions
- Area
- Shape
- Boundaries
Factors of By laws:
- Built up area
- Restricted height
- Setbacks
- Parking
- Allowable usage
- FAR, BAR

- By laws is to be studied from the local government development authority for understanding prevailing by law

Natural physical features:
- It includes different landforms of site and its characteristics
- To analyse the placement of different activities of site w.r.t. the existing features.

Components of site:
- Geology
- Topography
- Seismic zone
- Geo-hydrology
- Flora & Fauna
Geology:
- Earth science comprising study of solid earth.
- To assess the nature of soil and in turn the stability of land and its effect on the building.
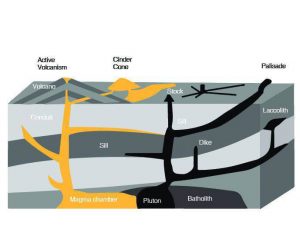
Factors of Geology:
- Soil type
- Bearing capacity
- Stability
- It can be analysed according to type of soil.
- As coarse grained soils has good bearing capacity.
- Strip foundation is recommended.
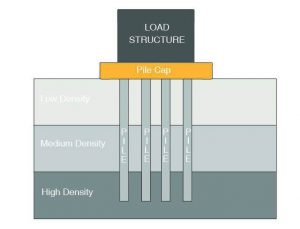
 b. Fine Grained Soils (eg. Silts and Clays)
b. Fine Grained Soils (eg. Silts and Clays)
- It has good-load bearing qualities when dry
- Pile foundation is recommended.
Topography:
- Slope and level of the land.
- To understand allocation of activities w.r.t topography.
Factors of Topography:
- Contour map
- Ridges, Valleys, Slope or flat
- Low point and high point
- To study topography through different slope of the land.
- One must consider the locations and elevations of different activities on and around the site.
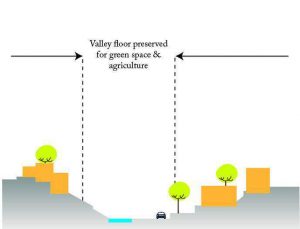
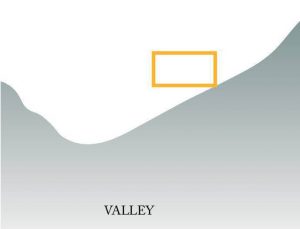
 b. Valley
b. Valley
- Catchment areas should be planned accordingly
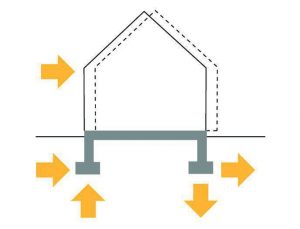
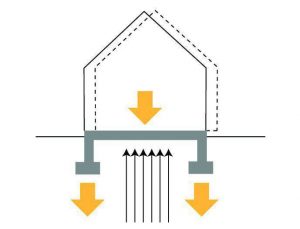
Seismic zone:
- Seismic zone is a region in which the rate of seismic activity remains fairly consistent
- To ensure structure and stability of building depending upon these seismic activities
Factors:
- Land
- Earthquake
- Landslides
- Volcano
- Water
- Floods
- Cyclones
- Tsunami
- Wind
- Hurricane
- Tornado
Geohydrology:
- It refers to study of ground water
- To analyse the effects of the water table, soil porosity, seepage, soil strength and how it affects the building.
Factors of Geohydrology:
- Groundwater level
- Sources/Modes of water
- Characteristics of water
Flaura and Fauna
- Available vegetation like trees, crops etc and living organisms like insects , termites etc
- To understand the influence of flora and fauna on project development.
Man made features:
- Things that are created or caused by humans rather than occurring naturally on and around the site
- To understand the influence of man made features for the development of the site
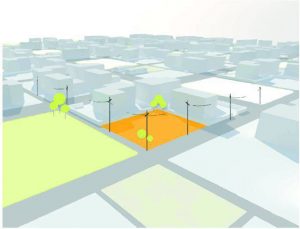
Factors of man made features:
Note: Data should be supported with maps, plans, elevations and sections, isometrics or perspective and relevant photographs.
All information is pertinent to your project.
- On site Features which may present on the site.
- Structure
- Paving patterns
- Power poles
- Hydrants
- Off site Features which may available in the nearby surrounding area.
- Electricity poles
- Water lines
- Sewer lines
- Telephone lines