-
Site planning is the organisation of activities on land according to site characters.
- Research and analysis makes a major contribution in site planning and later in design process.
Or
- "Site Planning is the art and science of arranging structure on the land and shaping the spaces between"

Why there is a need of Site Planning?
- To efficiently utilize site and conditions (analysed in site study) for better development of the project
- To set the relation between following factors:
Natural factors (Landscape)
Socio- economic factors (Planning)
SITE PLANNING ELEMENTS
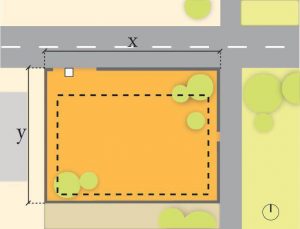
1. Site
- Site boundary
- Site dimensions
- Setbacks
- Orientation
- Existing Man made and Natural features on site
- Easements
- Adjoining/Important structures
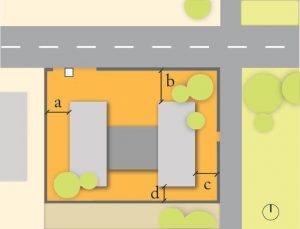
2. Building
- Placement of building
- Distance between buildings and site boundary/setback
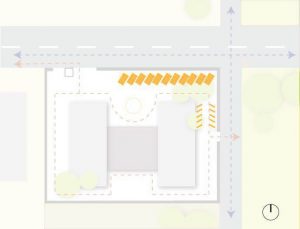
3. Parking
- Public
- Visitor
- Private
- Handicapped
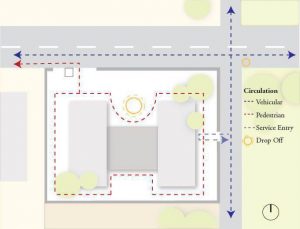
4. Accessibility and Circulation
- Vehicular (Street and site entrances)
- Pedestrian ( Site and building entrances)
- Services
- Emergency
- Drop off
- Other circulation (Bike ways, Public stops)
5. Landscape
- Softscape (Trees, shrubs etc)
- Hardscape (pavements, promenade etc)
- Furniture such as benches, light polls, sheds etc
- Fencing, walls or gates
- Open spaces (active passive and conservative areas)
- Other components such as bollards, signage, litter bins etc
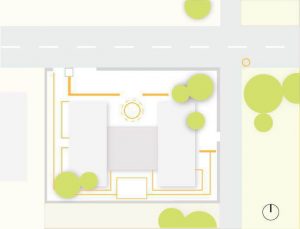
6. Utilities
- Drainage
- Water
- Gas
- Electricity
- Manholes
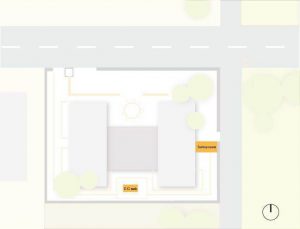
7. Views
- Prominent views from the site
- Prominent views to the site

Note : Data should be supported with maps, plans, elevations and sections, isometrics or perspective.
All information is pertinent to your project