Fabric or cloth can be defined as a flexible material comprising a network of natural or artificial fibres.
RELATED VIDEOS
Manufacturing of fabric
FIBRE
It is a long, thin strand or thread of a material.

YARN
They are natural or manufactured fibres that are twisted together and woven into a fabric.

FABRIC
They are cloth materials produced by weaving or knitting threads together.

Characteristics of good fabric
1. Fire Resistance
- Fabric applied with a flame coating can tolerate an extremely hot point source. However, a large ignition source may cause burning.
2. Design Flexibility
- Elasticity, durability and strength of textile structures allow them to accommodate loads ,and offer flexibility in designing.
3. Colour fastness
- With PVC-coated and PVC-laminated polyesters, colour selection affects the colour fastness and UV resistance of the finished material.
4. Good resistance to pilling and fading
- Fabric or textile structures are made to have a certain degree of resistance against pilling and fading.
5. Strength
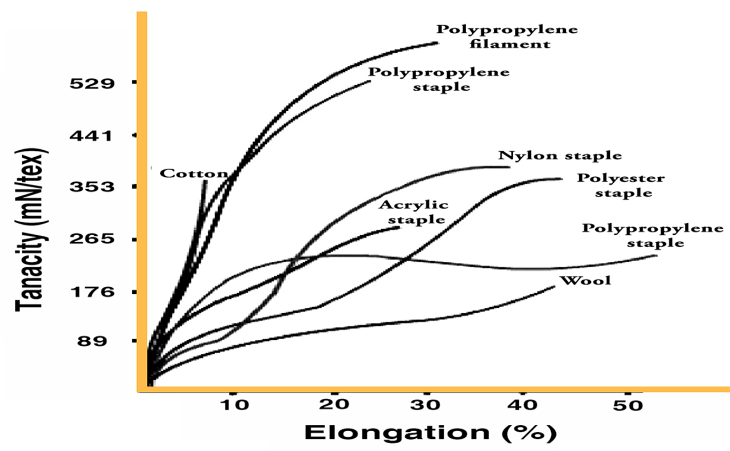
- Tensile strength is a basic indicator of relative strength of the fabric.
- Shear Strength demonstrates the capacity of the fabric to avoid rupturing. .
- Adhesion strength is a measure of the bonding capacity between the substrate and coating or laminate that protects it..
- Form Tensile fabric allows one to use free forms in construction because of its flexibility.
6. Structural properties
- Fabrics possess certain structural properties, some of these are:
- a. Stress versus Strain (unit load versus unit elongation)
- b. Expected service life
- c. The mechanism of material bonding(welding, gluing, etc.)
- These describes the fabric in terms of stiffness, elasticity, and plasticity.
Types of fabrics

a. According to Origin
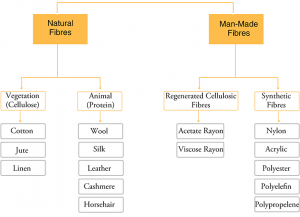
1. Natural Fibres
- Raw materials derived from plants, animals or minerals into non woven fabrics such as felt or paper or, after spinning into yarns, into woven cloth.

2. Man-Made Fibres
- Fibres whose chemical composition, structure, and properties are significantly modified during the manufacturing process.

3. Regenerated Cellulosic Fibres
- Fibres derived from cellulose obtained in a changed form by chemical treatment.
4. Synthetic Fibres

- Polymer based fibers, man made from chemicals and are stronger than natural and regenerated fibers.

b. According to Usage
According to the usage, fabrics may be classified into:
- Interior
- Exterior
Role of fabrics in interiors
- Fabrics protect paints and furnishings from damage due to harsh sunlight.
- Fabrics offer privacy to occupants.
- Incorporating fabrics can make a room cooler and reduce the air conditioning load in the summers.
- Besides providing a certain degree of thermal insulation, they help dampen noise and echo.

Major Interior Application Areas
1. Fabrics for seating
- Sofa covers
- Chair cushions
- Chair pads

3. Fabrics for walls
- Wall hangings
- Wall papers
4. Fabrics for Beds
- Bed sheets
- Pillow cases
- Blankets
- Mattress cover
- Dust ruffles

5. Fabrics for Bathrooms
- Shower curtains
- Terry towelling

6. Fabrics for home accessories
- Floor cushions
- Lamp shades
7. Fabrics for table
- Table cloths
- Table mats
Common fabrics used in interiors

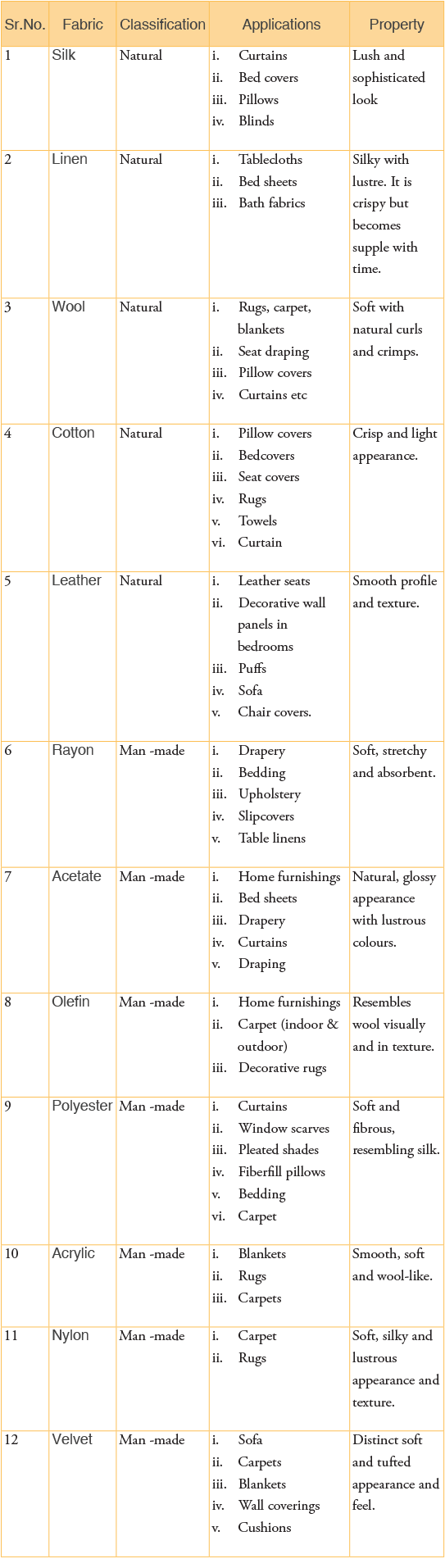
1. Silk
- It is among the strongest natural fabrics in the world.
- It is derived from the cocoon of the silkworm moth.
- It is lightweight, soft to touch and has a naturally lustrous texture.
- It is a high quality fabric providing comfort in all weather conditions.

Applications
- Curtains
- Pillows covers
- Exotic bed coverings, etc.

Advantages
- Available in a variety of weights and textures.
- Rich and sophisticated appearance.
- Strong and Lightweight.
- Resists wrinkles, mildew.
Disadvantages
- Spoiled by perspiration, deodorants, perfumes and hairspray.
- Weak when wet and sensitive to light.
Care
- Dry cleaning is preferred, some fabrics may be hand washed. Colours are prone to fading.
- Rubbing the surface damages the fibers. It is suggested to iron the back side at moderate temperature.
2. Linen
- Linen is a natural fibre derived from the flaxplant. It is one of the oldest fibres in use.
- It provides a tough yarn which has a smooth and glossy appearance.
- It is moth resistant and hardwearing.
- It is strong, easily washable and dries faster than cotton.

Applications
- Tablecloths
- Bed sheets
- Bath fabrics, etc.

Advantages
- It absorbs and releases moisture fast.
- It has a natural lustre.
- It is able to withstand high temperatures.
- It is stronger than cotton.
- It blends well with other fibres.
Disadvantages
- It is prone to wrinkles.
- It does not dye well.
- It wears out in areas of abrasion.
- It has a tendency to shrink unless treated.
Care
- It may be machine washed and dried.
- Bleach weakens fibres.
- It can be dry cleaned and ironed at high temperatures.
3. Wool
- Wool is a natural fibre fleeced from sheep or other mammals and further refined through various processes.
- It has a natural colour, but it can be dyed in other colours as well.
- It is an excellent insulator and finds maximum use in colder climates.
- It is versatile and can be blended with synthetics, resulting in an improved fabric.

Applications
- Rugs, carpets and blankets
- Seat draping
- Pillow covers
- Curtains, etc.

Advantages
- It is resistant to static build-up.
- It is a strong and durable fibre.
- It is resilient and elastic due to natural crimp..
- It is absorbent and dyes easily.
- It has adequate wrinkle resistance.
- Its low density makes it suitable as a lightweight material.
- It is resistant to fading.
Disadvantages
- It has a tendency to absorb odour.
- It is prone to moth attacks.
- It is not washable unless properly treated.
- It is weak when wet or moist.
Care
- Wool is usually dry cleaned.
- May be machine washed if treated.
4. Cotton
- Cotton is a natural fibre derived from the seed pod of the cotton plant.
- It is comfortable and breathable, which makes it an excellent fabric to work with.
- Its characteristic properties include resistance to fading and other signs of wear and tear.

Applications
- Pillowcovers and bedcovers
- Seat covers
- Rugs
- Towels
- Curtains, etc.

Advantages
- Strong and Durable
- Versatile fabric
- Static Resistant
- Cost Effective
- Extremely cheap
Disadvantages
- It is vulnerable to mildew.
- It is not elastic in nature.
- It wrinkles easily without special finish.
- It is prone to staining and soiling.
- It shrinks unless treated or pre-shrunk.
- It is highly flammable unless treated.
Care
- Cotton is machine washable if it is colour fast.
- May shrink if washed or dried at high temperatures.
5. Leather
- Leather refers to animal skins that are treated and preserved with chemicals to make them usable for various purposes such as furniture, tools, clothing, etc.
- It has a distinct profile and texture, making it highly popular.

Applications
- Leather seats
- Decorative wall panels in bedrooms
- Puffs
- Sofa
- Chair covers, etc.

Advantages
- It offers a classic and timeless look.
- It remains durable if cared for regularly.
- It is strong, flexible and easy to clean.
- It does not retain odour.
- It is dust and mite resistant.
Disadvantages
- It may get damaged by exposure to water and direct sunlight.
- It also gets scratched and torn easily (in case a thin layer is used).
- It can be expensive.
- It offers limited colour options.
Care
- It can be cleaned easily with a damp cloth once a week.
- It must be kept dust free.
- For weekly care, a clean, soft lint-free cloth slightly dampened with distilled water can be used to wipe it gently.
6. Rayon
- Rayon is produced from processed wood pulp.
- It is also known as art silk, due to its resemblance to silk.
- It has a bright lustrous texture.
- It is more durable than silk.
- It is widely used due to its reasonable price and popularity as a draping material.

Applications
- Drapery
- Bedcovers
- Upholstery
- Slipcovers
- Table linens, etc.

Advantages
- It has great affinity to dyeing.
- It drapes well.
- It can be washed easily.
- It is highly absorbent.
- It is versatile.
- It has better durability than silk.
Disadvantages
- Easily shrinks in hot water, also loses strength when wet.
- It is highly flammable.
- It can be fade easily.
- It is heat sensitive.
- It supports mildew growth.
- It develops wrinkles easily, unless treated.
Care
- Usually, it is machine washable,
- It retains a better appearance if dry-cleaned.
- It must be ironed at lower temperatures.
7. Acetate
- Acetate is manufactured from wood pulp.
- After rayon, acetate is a common substitute of various natural fibres as it is versatile and inexpensive.
- It is further used in making of satins and other fibres.
Applications
- Home furnishings
- Bed sheets
- Drapery
- Curtains, etc.
Advantages
- Sophisticated feel and appearance.
- It is available in a wide range of lustrous colours.
- It dries relatively fast.
- It is resistant to shrinkage, moths and mildew.
- Special dyes have been synthesized for acetate fibre since it does not accept dyes ordinarily used for cotton and rayon.
Disadvantages
- Heat sensitive
- It has poor abrasion resistance.
- It wrinkles easily.
- It has low absorbency and strength.
8. Olefin
- It is combined with other materials to generate aesthetics along with function.
- This fabric is ideal for high traffic areas as well as for home decor i.e. in living rooms.
- It is comfortable and commonly used for furniture.

Applications
- Home furnishings
- Carpets (indoor & outdoor)
- Decorative rugs, etc.

Advantages
- It is strong.
- It is non-absorbent.
- It is resistant to stains.
- It is extremely colour fast.
- It is inexpensive.
Disadvantages
- It is heat sensitive.
- It is prone to crushing
- It offers limited colors & designs.
Care
- Most stains on the fabric can be removed by cleaning with lukewarm water and a mild detergent.
- Bleaches can be used if required.
- If fabric is laundered, it should be line dried or tumble dried with mild or no heat.
- It should not be ironed.
9. Polyester
- Polyester is usually blended with a number of fabrics.
- It is highly versatile and available in many textures.
- Polyester is resistant to wrinkling.
- This makes it suitable for sitting areas.

Applications
- Curtains,
- Window scarves
- Pleated shades
- Fiberfill pillows
- Bedding
- Carpets, etc.

Advantages
- It is soft and durable.
- It resists staining and soiling
- It is easily dyed.
- It blends easily with cotton.
- It resists wrinkling.
- It is versatile.
- It is resistant to stretching, abrasion and shrinking.
Disadvantages
- It is prone to static electricity build-up.
- It is heat sensitive.
- It easily absorbs oil and grease.
- It is prone to pilling.
Care
- It is usually machine washable
- Fabric softener should be used to reduce static build-up.
- Oily stains should be immediately removed with solvent or detergent solution.
10. Acrylic
- Acrylic used as an alternative to wool and it also being used as alternative to cashmere.
- It is soft and comfortable and its durability makes it an excellent choice for home decor.
- Generally, acrylic fabrics hold colour extremely well.
- It also resist stains and wrinkles.

Applications
- Blankets
- Rugs
- Carpets, etc.

Advantages
- It has the appearance and feel of wool.
- It resists mildew and moisture.
- It is lightweight.
- It is resistant to wrinkles, chemicals, oil and sunlight.
- It dries fast.
- It is elastic in nature.
Disadvantages
- It is prone to pilling.
- It builds up static electricity.
Care
- It is machine washable and dryable.
- A fabric softener is used to reduce static.
11. Nylon
- Nylon is a highly versatile, resilient fabric with silky texture.
- Being synthetic, properties such as durability and fading are addressed during manufacture.
- It can also hold colour well.
- It is however, strong in nature and used in blends instead of its pure

Applications
- Rugs
- Sheer Curtains
- Carpets, etc.

Advantages
- It is highly durable.
- It is soft and lustrous.
- It is very strong.
- It is easy to maintain.
- It resists matting.
- It dyes well.
- It is mold, mildew, and moth-resistant.
- It is abrasion resistant.
- It resists stretching and shrinking.
Disadvantages
- It attracts dirt.
- It is prone to pilling and fades easily.
- It builds up static electricity.
- It is heat sensitive.
- It does not absorb moisture.
- It may pill.
- White fabric may become gray or yellow.
Care
- It is machine washable.
- Fabric softener should used to reduce static.
- It should be ironed at low temperature.
12. Velvet
- Velvet is a kind of smooth woven tufted fabric, which may either be synthetic or natural.
- It is a luxurious fabric which finds use in home decor.
- It is suitable for furniture, pillow covers, as well as wallpapers.

Applications
- Sofas
- Carpets
- Blankets
- Wall coverings
- Cushions
- Pillow covers, etc.

Advantages
- It is soft and has a luxurious appeal.
- It is light.
- It offers good colour depth.
- It offers good insulation.
- It has decontamination ability.
Disadvantages
- It is difficult to clean.
- It is costly.
- The fabric wears out quickly with use.
- It is prone to dust absorption..
Care
- It should be washed with cold water and a neutral detergent should be used.
- After washing, the velvet should be tiled on a large bath towel. The moisture should be squeezed out after wrapping.
Natural vs synthetic fabrics
Natural Fabrics |
Synthetic Fabrics |
| Cotton
Versatile, Breathable and Affordable May wrinkle or fad |
Acrylic
Lightweight, Colourfast and does not fade Difficult to clean |
| Wool
Strongest and Durable Warm and cozy |
Nylon
Tough and long lasting, Not breathable and uncomfortable |
| Silk
Luxurious but Expensive The material fades over time if exposed to direct sunlight |
Acetate
Does not pill and wrinkle resistant. It is an ideal fabric for draperies. |
Role of fabrics in exteriors
The building fabric serves to:
- Protect the building occupants from elements of weather, such as wind, rain, solar radiation, snow, and so on.
- Regulate the thermal comfort of indoor environment.
- Provide privacy for occupants.
- Prevent noise transmission.
- Provide security for occupants and the building contents.
- Provide safety from hazards, for example by preventing the spread of fire or smoke.
- Provide access between the inside and the outside of buildings.
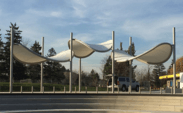
Common Fabrics used in Exteriors
- Cotton canvas
- Polyester
- Vinyl laminated polyester
- Vinyl coated polyester
- Fibreglass
- Blackout fabric
- Olefin
Note: Use of fabrics in exteriors varies with coating and lamination.
Major Exterior Application Areas
- Architectural membranes
- Hoardings and signage
- Scaffolding nets
- Awning and canopies
- Parking shades
- Tarpaulins