Elements of design is the form in order of their growth from :
Point to one dimensional Line, from Line to two dimensional Plane, from Plane to three dimensional Form or Volume.
Components of Element of Design
- POINT

- LINE
- PLANE

- VOLUME

1. POINT:
- Indicates a position in space.
- It has no dimension.
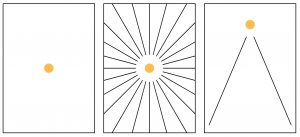
Point can serve to mark:
- The two ends of a line.
- The intersection of two lines.
- The meeting of lines at the corner of a plane or volume.
- The center of a field.
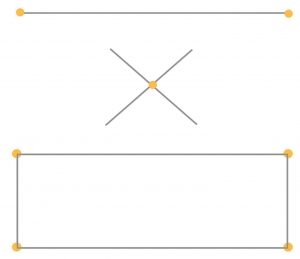
2. LINE:
- A point extended becomes a Line.
- Has only length dimension, but no width or depth.
- A line, in describing the path of a point in motion.
- Visually expressing direction, movement, and growth.
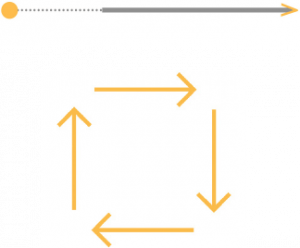
- Join, link, support, surround or intersect other visual elements.

- Define boundary and give shape to the plane.
- Articulate the surfaces of planes.
- Create perspective and depth and suggest movement.

Characteristics of Line:
- It is seen as a line simply because its length dominates its width.
- It must have some degree of thickness to become visible.
- It must have a degree of continuity.
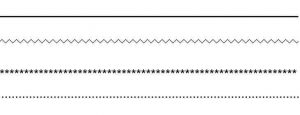
Types of Line:
1. Vertical Line
- Indicates: Dignity, Strength, Stability


2. Horizontal Line
- Indicates: Calm, Peace, Relax


3. Diagonal Line
- Indicates: Action, Activity, Excitement, Movement


4. Curved Line
- Indicates: Softness, Sooting, Freedom


3. PLANE:
- A line extended in a direction other than its intrinsic direction becomes plane.
- A plane has length and width, but no depth.
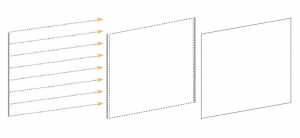
A Plane serves to make:
- Shape is the primary identifying characteristic of a plane.It is determined by the contour of the line forming the edges of a plane.
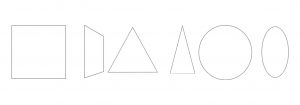
- The supplementary properties of a plane, its surface color, pattern, and texture affect its visual weight and stability.

- A plane serves to define the limits or boundaries of volume.

Three generic types of Planes:
- Overhead Plane
- Wall Plane
- Base Plane

In Nature:
In Architecture:


4. VOLUME:
- A plane extended in a direction other than its intrinsic direction becomes a volume.
- A volume has three dimensions: length, width, and depth.
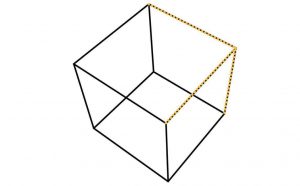
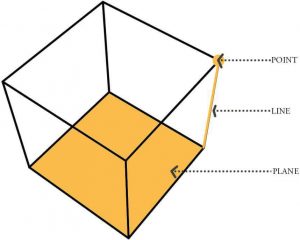
All volumes consist of:
- Points or vertices where several planes come together.
- Lines or edges where two planes meet.
- Planes or surfaces that define the limits or boundaries of a volume.
In Nature: