- Blockboard comprises of core of softwood strips or blocks between layers of veneer.
- The direction of grain of the blocks is perpendicular to that of the adjacent veneers.
- It should be noted that the core of blockboard runs length wise to gain maximum strength.
RELATED VIDEOS
Manufacturing of Blockboard

Note:
The softwood blocks are obtained by slicing timber logs, while the outer veneers are usually obtained by rotary-cutting of the logs.
In rare cases, manufacturers may also use hardwood blocks for the core. However, softwood, for example pinewood, is most commonly used for the core.
Properties of blockboards
1. Weight and Density
- Its density is lower than hardwood.
- Its lightweight property makes it easy to transport and handle.
2. Strength and Durability
- They are stronger than particle boards and MDF, but are weaker than plywood.
- They are less durable than plywood.
3. Resistance to Water
- They are relatively resistant to water, and can be made waterproof by using BWP (Boiling Water Proof) grade resin for bonding the strips.
4. Resistance to Warping and Cracking
- They possess excellent dimensional stability when subjected to humid conditions, and strongly resist warping and cracking.
5. Resistance to Sagging and Bending
- Their stiff structure ensures their protection against sagging or bending.
- It is preferable for furniture elements that are greater than 6'-7' in length.
6. Fitting
- Blockboards have excellent screw holding capacity.
- This makes them appropriate for custom made furniture.
7. Surface Finishing
- They are available in various finishes such as laminates, wood veneers, melamine finish, etc.
- They can also be painted and polished.
8. Ease of Working
- Blockboards are easy to work with, using regular woodworking tools.
9. Sound and Thermal Insulation
- They offer excellent sound and thermal insulation properties.
- They are used in partitions where soundproofing is required such as recording studios, radio stations, etc.
Uses of blockboard
1. For making tables, benches and wall furniture
2. For making blockboard doors and solid core flush doors
3. For making single and double beds and settees (divan)
4. For making long wall panels and partitions
Types of blockboard
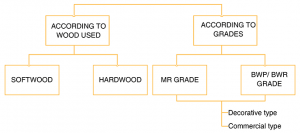
a. According to Wood Used
1. Softwood Blockboard
- The core comprises of solid blocks of softwood and veneers on outside.
- They are lighter, weaker and less expensive than hardwood blockboard.
2. Hardwood Blockboard
- This type of blockboards have a core made from hardwood strips and veneers on the outside.
- They are denser, heavier, stronger and more expensive.
b. According to Grades
1. MR Grade
Moisture resistant grade
- Special moisture resistant glues are used in the manufacture.
- They are also called interior grade blockboards, as they are used for doors, partitions, paneling, furniture making, ceiling, etc.
2. BWP or BWR Grade: IS: 1659
Boiling water proof or Boiling water resistant grade
- These are manufactured using resins having high resistance to boiling water.
- They are also called exterior grade blockboards. as they are used in prefabricated houses, railway coaches, bus bodies, kitchens, etc
Decorative type:
- Composition: Decorative face veneers on one or both sides
- Uses: High quality furniture, interior decoration, paneling, partitions, etc.
Commercial type:
- Composition: Veneers of timber on either side Uses: Simple furniture, tabletops, partitions, paneling, seats in buses and railway coaches, etc.
The grades and types of block boards are represented by the symbols below:
Grade and Type |
Symbol |
| BWP Grade, Decorative type | BWP-DEC BWP Grade |
| Commercial type | BWP-COM MR Grade |
| Decorative type | MR-DEC MR Grade |
Available sizes and thickness of blockboard
Sizes:
Blockboard Size (in sq.feet) |
Corresponding size in mm (rounded values) |
| 8' x 4' | 2440 x 1220 |
| 8' x 3' | 2440 x 915 |
| 7' x 4' | 2135 x 1220 |
| 7' x 3' | 2135 x 915 |
| 6' x 4' | 1830 x 1220 |
| 6' x 3' | 1830 x 915 |
Thickness:
According to IS Code 1659, blockboard thicknesses are:
Blockboard Size (in sq.feet) |
| 12mm |
| 15mm |
| 19mm |
| 25mm |
| 30mm |
| 35mm |
| 40mm |
Note:
The blockboard thicknesses mentioned above include that of the softwood core blocks in addition to the front and back face veneers. The veneer layers glued on each side of the core are generally 4 mm thick. Thus a 19mm blockboard has roughly 8mm worth of hardwood layers and an approximately 11mm thick softwood core.
Precautions while assembling blockboard
- Strips of suitable thickness are carefully sandwiched between the veneers.
- The strips should be glued under high pressure.
- While placing softwood, no gap should form between the strips.
Advantages of blockboard
1. Light-weight
- Their less weight ensures easy transportation, reducing transport costs.
- In interiors, they are commonly used in doors due to their light weight.
2. Cheap
- They can be used as a cheaper alternative to plywood in interiors.
3. Resistance to sagging or bending
- It has a stiff structure, making it suitable for crafting long furniture items i.e. > 5?, such as panels, book shelves, tables, benches, etc.
4. Strong and durable
- Blockboards are stronger and have better durability compared to MDF and particle boards.
Disadvantages of blockboard
1. Weaker than solid wood
- The major component in blockboard is derived from softwoods, making it less desirable in strength and quality compared to solid wood (such as teak wood) or hardwood plywood.
2. Danger of compromised nail holding capacity
- The blocks may occasionally have tiny gaps between them which are not visible since there is layer of veneer on top.The nails driven through the board surface may penetrate the gap, which can endanger the holding strength of that nail.